|
|
5 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| include | 5 years ago | |
| old | 5 years ago | |
| profiling | 5 years ago | |
| src | 5 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 5 years ago | |
| LICENSE | 5 years ago | |
| Makefile | 5 years ago | |
| README.md | 5 years ago | |
| TODO.org | 5 years ago | |
| test.sh | 5 years ago | |
README.md
shuffle3-lean - Improved 3 stage byte shuffler
Deterministically and reversably shuffle a file's bytes around.
Shuffling
Shuffle a file in place
$ shuffle3 -s file
Unshuffling
Unshuffle a file in place
$ shuffle3 -u file
Other options
Run with -h for more options.
Improvements from v1
- ~70-80x speedup from shuffle3 v1.0
- Huge reduction in syscalls
- Takes advantage of the kernel's fs cache
- Can properly handle large files without core dumping
- Doesn't dump huge amounts of trash onto each stack frame
Performance
hyperfine reports a 700-800% speedup over v1.
It's easy to see why.
V1 flamegraph
V1 uses a pesudo-array adaptor to perform filesystem reads, seeks, and writes. This causes a massive syscall overhead.
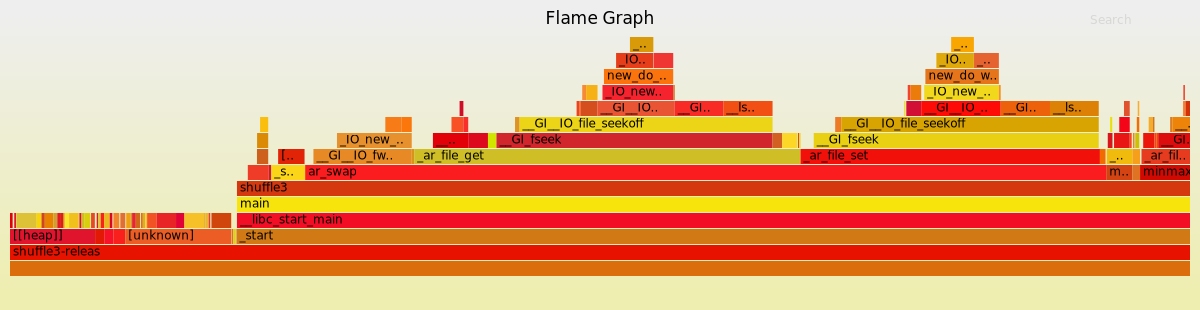
V2 flamegraph
Whereas V2 uses a single mmap().

Memory usage
The memusage graph for =v1= shows extremely inefficient stack usage.
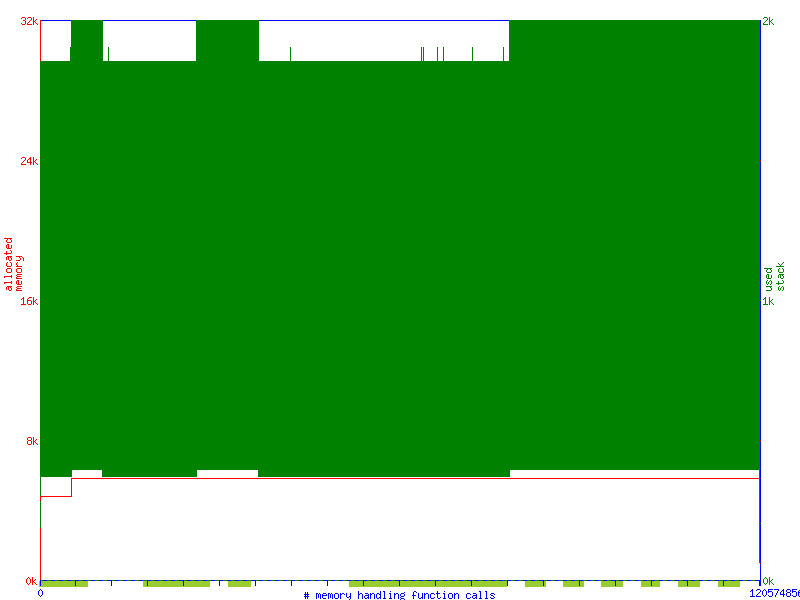 ( the green is supposed to be a line, not a bar )
This is due to how the unshuffler buffers RNG results.
( the green is supposed to be a line, not a bar )
This is due to how the unshuffler buffers RNG results.
v1 naively used VLAs to store this buffer, which can baloon to 8 times the size of the file being unshuffled.
It dumps this massive buffer onto the stack frame of a function that is called multiple times, causing massive and inefficient stack usage.
This can cause a segfault when attempting to unshuffle a large file, while shuffling a file of the same size might succeed.
V2 improvement
The memusage graph for v2 is a lot more sane.

v2 instead allocates this buffer on the heap. Note the stable stack and heap usage.
Building
Run make to build the normal binary. It will output to shuffle3-release.
Release target
The release (default) target uses the variables RELEASE_CFLAGS, RELEASE_CXXFLAGS and RELEASE_LDFLAGS to specify opitimisations, as well as the OPT_FLAGS variable. These can be set by you if you wish.
Note
The default OPT_FLAGS contains the flag -march=native. This may be underisable for you, in which case set the variable or modify the makefile to remove it.
Debug target
To build with debug information, run make debug. Extra debug flags can be provided with the DEBUG_CFLAGS, DEBUG_CXXFLAGS and DEBUG_LDFLAGS variables which have default values in the Makefile.
The build and unstripped binary will be shuffle3-debug.
Notes
Before switching between release and debug targets, remember to run make clean.
To disable stripping of release build binaries, run with make STRIP=: release
License
GPL'd with <3